Authors:
Rodrigues Jr, Manoel T. 1; Santos, Hugo 1 ; Zeoly, Lucas A. 1 ; Simoni, Deborah A. 2 ; Moyano, Albert 3 ; Coelho, Fernando 1
Abstract:
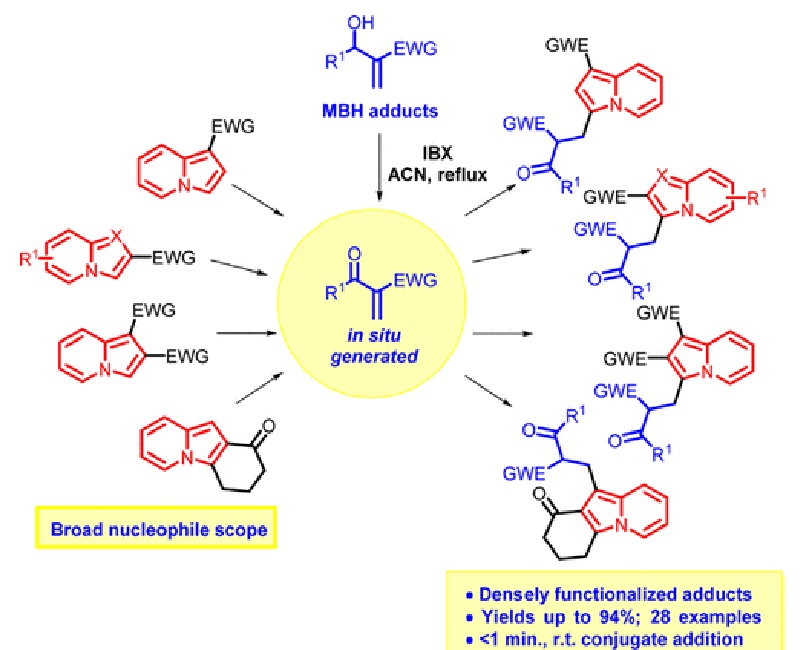
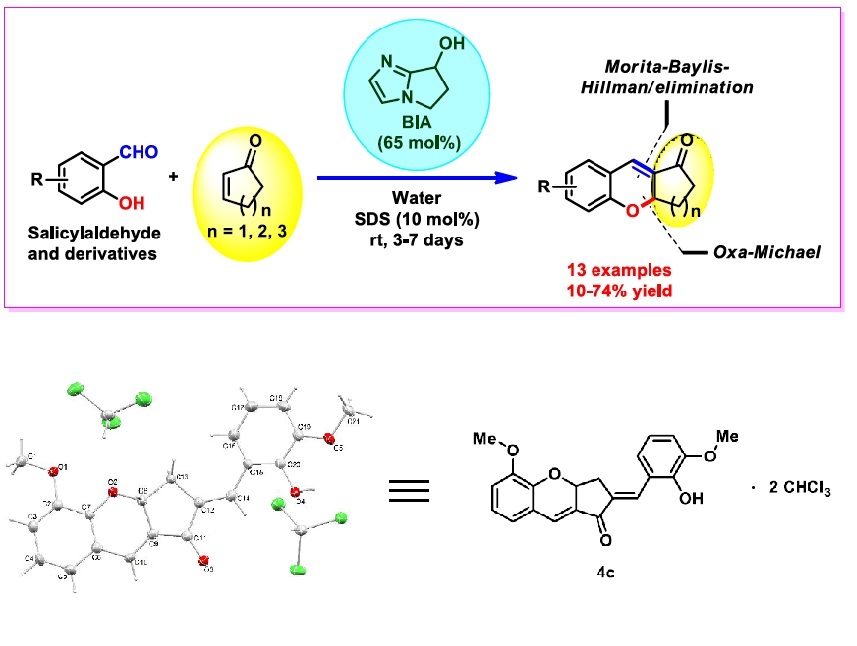
The Morita-Baylis-Hillman (MBH) reaction is a carbon-carbon bond forming transformation between an electrophile, typically an aldehyde, and an activated olefin. MBH adducts obtained from 2-hydroxybenzaldehydes and cyclic enones are potential substrates for the synthesis of xanthenone and chromenone derivatives. In this work, we investigated conditions to obtain tetrahydro-1H-xanthen-1-ones and chromen1-ones directly via a Morita-Baylis-Hillman/oxa-Michael/elimination cascade catalyzed by a bifunctional, bicyclic imidazolyl alcohol (BIA), which proved to be an effective catalyst for this transformation. The reactions were performed at room temperature in water to give the products in 10-74 % yield
1 Laboratory of Synthesis of Natural Products and Drugs, Institute of Chemistry, University of Campinas, UNICAMP, P.O. Box 6154, 13083-970, Campinas, SP, Brazil
2 Laboratory of Crystallography, Institute of Chemistry, University of Campinas, UNICAMP, P.O. Box 6154, 13083-970, Campinas, SP, Brazil
3 Secció de Química Orgànica, Departament de Química Inorgànica i Orgànica, Facultat de Química, Universitat de Barcelona, Martí i ̀Franquès 1-11, 08028 Barcelona, Catalonia, Spain
Link to article: https://www.arkat-usa.org/arkivoc-journal/browse-arkivoc/ark.5550190.p011.133